
If the f-value is greater than or equal to the variation between the groups, the null hypothesis holds true. The f-value shows the significance of the mean differences, indicating whether the variance between the groups forms a relationship. This statistical test measures the difference in means for two or more independent samples.
#NULL AND ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS TEST CALCULATOR HOW TO#
Read more: How To Calculate P-Value in Excel Using Two Methods F-valueĪn f-value is a test statistic that you can get from an analysis of variance (ANOVA). It's important to note that p-values depend on the results t-tests give you and can change according to different t-statistics. Comparing the result to a respective alpha level gives you the estimate for the p-value. Taking the sample size n, subtract one to get the degree of freedom (n - 1). The p-value is a probability measure and uses the degree of freedom and estimation based on the alpha value of a t-test. Measuring a smaller p-value suggests the rejection of the null hypothesis, whereas a higher p-value indicates stronger evidence for supporting the null hypothesis. It's a metric that argues against the null hypothesis and relies on the alpha value, critical value and probability. The p-value in a statistical test helps you determine whether to reject or support the null hypothesis. Read more: How To Calculate a Z-score P-value Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X represents the raw data or score, μ is the mean of the population and σ is the standard deviation for the population. To get the z-value, you can use the formula: This allows for the comparison of two z-values from different sample groups with varying standard deviations and mean values. The z-score is also important for calculating the probability of a data value appearing within the normal distribution for a specific standard. This metric goes beyond the t-value, which tests only a sample of the population. The z-value is another common test statistic where the null hypothesis suggests the means of two populations are equal. Read more: What Is a T-Test? (Definition, Purpose and How To Calculate) Z-value
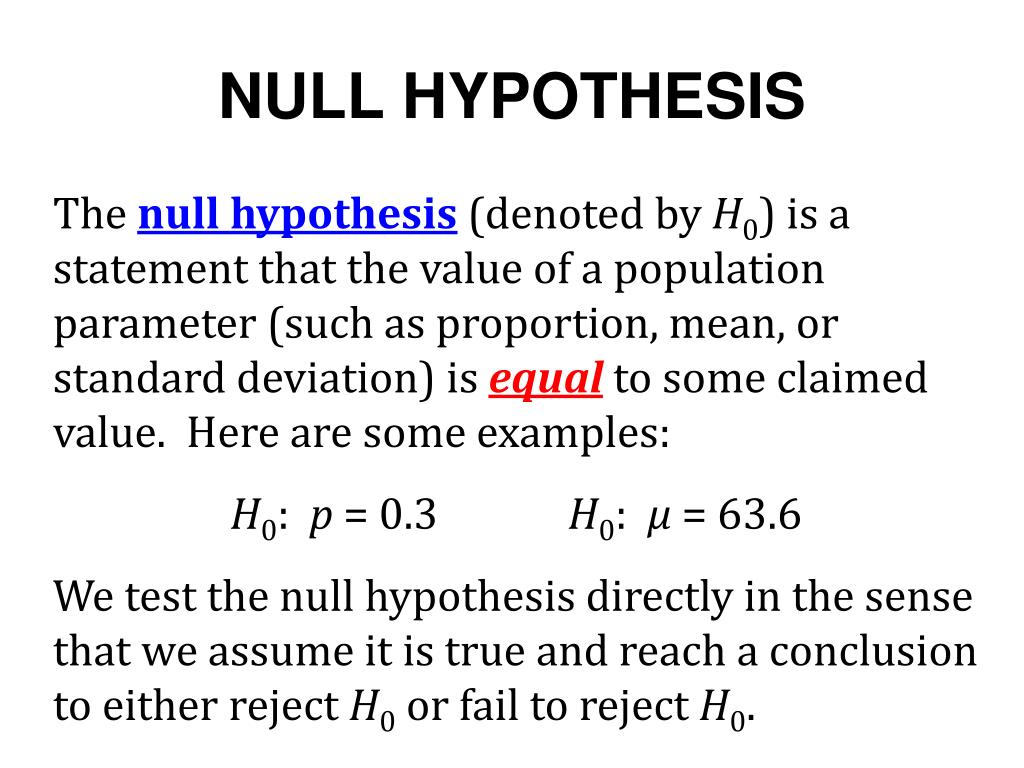
T = (X‾ - μ0) / (s / √n), where X‾ is the sample mean, μ0 represents the population mean, s is the standard deviation of the sample and n stands for the size of the sample. You can calculate a t-value using a common t-test with the formula: If you perform a t-test or regression rest and find the means are not equal, you reject the null hypothesis for the alternative hypothesis. Evaluating the t-value requires testing a null hypothesis where the means of both test samples are equal. The t-value is one type of test statistic that results from performing either t-tests or regression tests. The following test statistics are some of the common applications data professionals use when performing statistical analysis: T-value Related: How To Calculate Statistical Significance (And Its Importance) Types of test statistics If you arrive at an alternative hypothesis during statistical analysis, it can indicate a rejection of the null hypothesis. When performing statistical tests, the goal becomes to either reject the null hypothesis or prove it correct.Īlternative hypothesis : Alternative hypotheses propose that there is a significant difference between two samples and the variations between the groups result in unequal means.
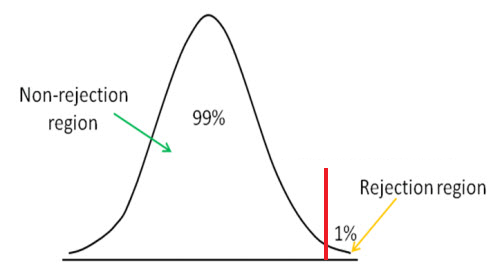
Null hypothesis : This hypothesis proposes that the means of two distinct sample groups are equal. To better understand different test statistics, it's important to distinguish between what a null and an alternative hypothesis are: The distribution of data accounts for the frequency at which observations occur when performing statistical tests and shows the central tendency and variation.īecause there are different statistical tests you can use to analyze data distribution, the central tendency and variance measures differ based on the type of hypothesis you predict for a certain test. The statistic depends on what kind of data analysis method you use and indicates how closely your data matches the predicted distribution for the specific test you perform. What is a test statistic?Ī test statistic measures the accuracy of the predicted data distribution relating to the null hypothesis you use when analyzing data samples.

In this article, we explore what a test statistic is, what types of test statistics there are and how to calculate a test statistic using two of the most common values, with helpful FAQs for additional insight. These test statistics result from the specific analysis you perform when studying data. Depending on the outcome researchers are looking for, the data can display one of many test statistics.

In statistics, researchers perform various tests to further analyze their data. Researchers discuss calculations on a writing board.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
